Architecture
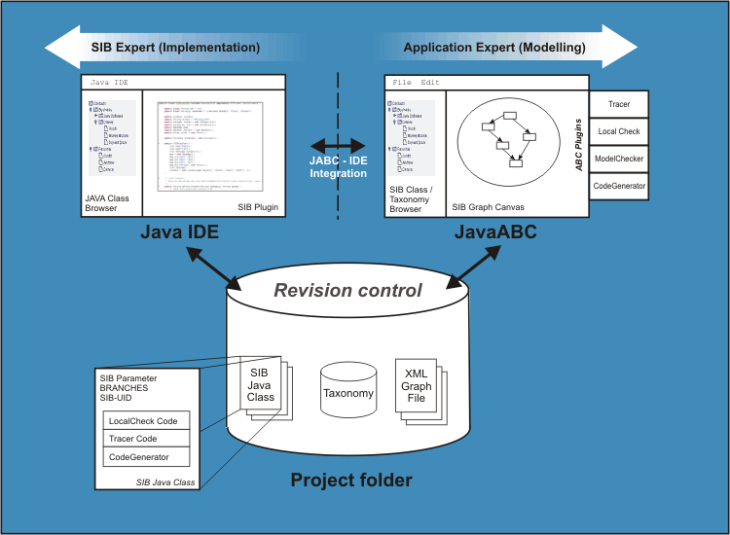
jABC is a platform independent, graphical, component based, modeling tool. The
core of the system is the jABC Framework. All essential features of the system
are part of this Java framework. The complete system consist of the following
elements:
- jABC / the modeling application
- IDE / the development application
- RCS / a revision control system
jABC
jABC is the editor for the graphical-based development method called
Lightweight Process Coordination. After a short training a user can model a
system from existing components on his own with the jABC. Using the graphical
input of the jABC is very easy especially for the so called application expert
which means a user with a special know-how on a specific problem or domain but
without classical programming knowledge. The editor is fitted with a plugin
interface. Plugins can add new menu entries, popup menus or inspector panes.
Main function of a plugin is to add semantics to a jABC graph model. A model
can be interpreted as a controlflow graph, callgraph or totally different
depending on the installed plugins.
The editor consists of the following parts:
- Project and taxonomy browser
- Drawing canvas
- Inspector panel
- Plugin interface
The components used within jABC are called SIBs (Service Independent Building
Blocks). The SIBs are presented in a structured view to the user called
the SIB taxonomy. SIB represent the vertices of the jABC graph model. The
directed edges are called branches. Multiple branches can be attached to a
single edge to reduce parallel edges.
IDE
The implementation of a SIB component for the system is the task of the SIB
expert. The collection of the SIB components is fundamental for the jABC
system. On the other hand this is the essential difference to all previous
versions of ABC systems. jABC consolidates the different computer languages for
the description of a component in older ABC version to a single language: Java!
In jABC a SIB is a simple Java class implementing a quite simple interface. The
class file summarise all abstract implementions of a component including the
real world implementation for this SIB.
The task of the SIB expert is to implement the SIB Java classes. Technically
every compiler can be used to produce these Java classes. The selection of a
development environment can be freely done by each SIB expert on his own. It is
not necessary that all SIB experts use the same development environment.
With IDEs like Eclipse a close integration with the jABC guarantees a quick and
simple creation of new modeling components.
RCS
The central communication server in the jABC system is any Revision Control
System like CVS or SVN. The RCS server supplies all elements of a project to
the different participants of a project. The rights and role management of the
RCS system controls the availability of different files to the project users.
Additionally any file needed for the project (but not especially for the jABC)
can and should be stored in the RCS Only by maintaining such a centralized
versioning system guarantees to extract consistent snapshots of older versions
of a project or model.
In principle almost every versioning system can be used as the central
communication server in the jABC system. We currently use Subversion because it
is widely known and it is supported by the other tools of the project like
Netbeans or Eclipse.
